Car Cooling System
A comprehensive guide to what a car cooling system comprises of and its function in an internal combustion engine.
Why do we need a cooling system in our cars?
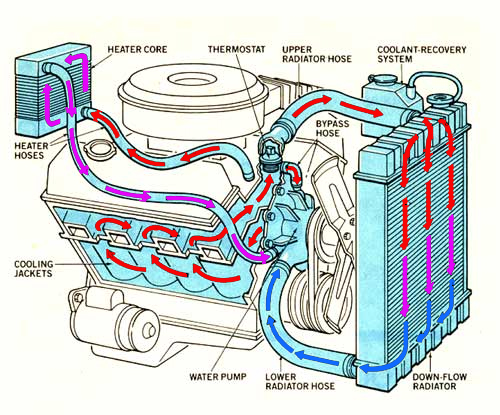
Overview
The car cooling system uses one of Earth’s most precious Elemental Resources, WATER, (H2o), to keep our car’s engine running at normal operating temperatures at between 80-95 Degrees Celsius.
Overheating is considered to be any temperature over water’s boiling point at 100 degrees Celsius.
To prevent your car’s engines from overheating a car cooling system is incorporated into the car to regulate the temperature at which a car’s engine needs to operate at optimum levels and is made up of a few main components:
- Coolant Expansion Tank
- Expansion Tank Cap/Radiator Cap
- Radiator
- Radiator Fan
- Fan Belts
- Water Pump
- Water Pipes (Hoses)
- Thermostat
- Temperature Sender Switch
- AntiFreeze
We will look at the function of each and learn the role it plays in keeping our vehicle’s engine operating at normal operating temperature.
(In simple terms)
Coolant Expansion Tank

Its function is to feed the Radiator with coolant.
Older model cars do not use an expansion tank, and have open overflow systems directly from the radiator to the ground; most modern cars do incorporate Coolant Expansion Tanks.
It is usually made of a high temperature resistant white, black or transparent plastic material with metal inserts at strategic points for strength, some are made of Aluminium or other non-corrosive metals.
The Coolant Expansion Tank is where we fill our cooling system with coolant and periodically check our engine coolant levels.
Cracks in the Coolant Expansion Tank due to age, and perished pipes, connected to the Coolant Expansion Tank leads to coolant loss and when not detected in time, may cause overheating.
Expansion Tank Cap / Radiator Cap


Its function is to seal the cooling system.
It is usually clipped or screwed on to the tank/radiator, incorporating a pressure valve which opens at approximately 16-22 (psi), allowing for the release of cooling system pressure when the engine reaches normal operating temperature. (Coolant expands when heated, increasing pressure).
An Expansion Tank Cap is made of high-temperature-resistant plastics with rubber seals, whereas a Radiator Cap is made of metal with rubber seals.
When the Expansion Tank Cap/Radiator Cap malfunctions it leads to overheating and/or coolant loss. Regular coolant level checks are advised.
Radiator
Its function is to cool hot water being transferred from the engine.
This is achieved by its construction of horizontal or vertical water tubes attached to thousands of tiny cooling fins made of copper or aluminium which are bad conductors of heat, this is known as the Radiator’s core.
The Core is attached to 2 water tanks made of high heat resistant Bakelite or Plastic which in turn are connected to the engine via inlet and outlet ports.

(In earlier years Radiators were made of Copper, both the Tanks and the Core).
Air flows over the tiny fins which in turn cools the tubes as the coolant passes through the radiator. This process is repeated as long as the car engine is running and is commonly known as coolant circulation.
An electrical fan is attached to the car radiators, which is thermostatically controlled to activate at preset temperatures blowing cool air over the radiator’s core. Older model cars use a fixed mechanical or viscous fan attached directly to the water pump to achieve this.
Radiators are mostly mounted in the front of the car just behind the grill. While driving the forward motion of the car creates cool air to pass through the grill and over the cooling fins of the radiator, therefore the radiator cooling fans are mostly only useful in slow-moving/heavy traffic or when idling our cars for extended periods.
Radiator cores deteriorate with time and its cooling fins become brittle and start to disintegrate reducing its cooling abilities, the core tubes develop leaks over time, which may lead to overheating when not detected.
Radiator Fan


Its function is to blow cool air across the Radiator Core to cool down the car’s coolant.
The fan is sometimes fixed to the water pump pulley, driven by the Fan Belt and constantly draws heat from the Radiator’s core while the engine is running.
In other designs it is attached directly to the radiator core and fitted with an electric motor to blow away heat from its core, it is activated by a thermostatically controlled switch in the car’s cooling system.
When the fan blades break off it can cause damage to the radiator core and other car parts in close proximity and overheat the engine. When its bearings are worn it will cause unusual noises in the engine and have excessive play.
Fan Belts
Its function is to transfer power from the car’s engine via the crankshaft pulley to the water pump pulley.
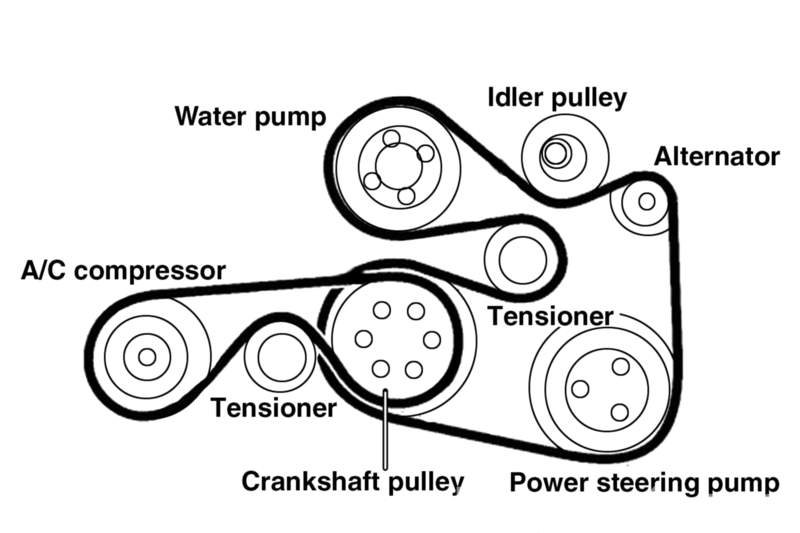
It is made of a rubber compound incorporating thin fibre strands for reinforcement and strength, it comes in various sizes and design formats, namely V-belt, Ribbed-belt and toothed-belts. When it breaks the car will overheat because the water pump is no longer circulating coolant in the cooling system.

Water Pump

Its function is to pump the coolant from the radiator through the engine and back to the radiator.
It is made of Aluminium, Cast Metal Alloys and sometimes Plastics, with steel or plastic impellers and steel shafts. The water pump is mostly attached to the engine having direct access to the engine water ports which surrounds the crank and piston assemblies.
Some vehicles make use of additional auxiliary electric water pumps to assist in the circulation of coolant in the cooling system, mostly specialized vehicles.
Water Pipes/Hoses

Its function is to connect various cooling system components to each other in order for these components to function as one efficient cooling system.
It is usually made of rubber with reinforced fibre strands much like fan belts but much more pliable, other water pipes are made of metal or plastic with rubber o ring seals. The pipes are mostly kept in place by hose clamps constructed of high tensile steel. When they burst or leak, water loss is imminent causing overheating.
Thermostat
Its function is to regulate the temperature of the coolant in the car’s cooling system.
It acts as a gate to contain coolant in the engine until the coolant reaches a normal operating temperature between 80-95 Degrees Celsius and allows the coolant to flow to the radiator to be cooled, thus transferring heat from the engine.
It is usually made of Steel, Copper, Aluminium, Rubber and Wax. The Wax is contained in a chamber which when heated, expands to activate a gate, in the form of a metal disc which in turn allows the heated coolant to pass from the engine to the Radiator.
The Thermostat will stay in its open state until the water cools down sufficiently to cause it to close again, usually after the engine is shut off and cools down.
In older vehicles when it malfunctions it sticks in a closed state causing the car to overheat, modern cars, however, have a fail-safe built into the thermostats causing it to get stuck in an open position, preventing overheating of the car’s engine, but causing it to run much cooler than it normally should.
Temperature Sender Switch

Its function is to send a signal to the temperature gauge in your car’s dashboard enabling you to monitor the operating temperature of your vehicle.
It is usually made of Brass and Bakelite, part of it is immersed in the engine’s coolant in order to send a signal to the dashboard’s temperature gauge.

It functions much like a thermostat in that it uses wax contained in a chamber which expands when heated to complete an electrical circuit. It could malfunction causing inaccurate temperature readings and/or water loss.
Antifreeze
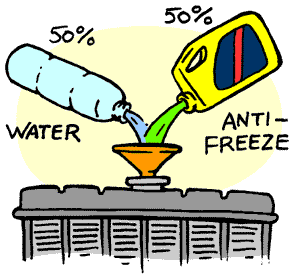
It is advisable to add Antifreeze to your cooling system, which not only helps regulate Coolant Temperatures but also lubricates the internal parts of the cooling system, preventing Rust and Scale build-up, prolonging Water Pump life. It comes in various colours, such as Red, Green and Blue.
In certain Countries, snow occurs in Winter, Antifreeze prevents the coolant from freezing and causing the Engine Block to crack due to the expansion of the freezing coolant.
So ensure that your car’s coolant is treated with Anti Freeze, particularly if you purchased it recently, in Summer.
Conclusion
All these components make up the whole of your cooling system, it is important to check on these main components regularly especially as your car ages. Ensure that your Auto Mechanic checks on your cooling system at your scheduled service intervals as well.
3 Important Checks To Remember Doing Regularly On Your car
I hope that I have fulfilled my intention of leaving you a little more informed about your car’s cooling system.
What are your thoughts, has this information been helpful? Comment below
Until Next Time “Safe Motoring”



The primary job of a cooling system in an automobile is to prevent the engine from overheating. The engine in the car runs best at a fairly high temperature. Another important job of car’s cooling system is to allow the engine to heat up as quickly as possible and then to keep the engine at constant temperature. A car’s cooling system comprises of various components such as radiator, water pump, thermostat, bypass system, hoses and heater etc. It is advisable to check the different components of the cooling system properly by a professional in order that it will run perfectly without any mechanical problem.
Thanks for visiting my website and your insights into a cars cooling system all of which is covered here in this detailed post.
Gary
I would like to thank you for sharing such useful information about the cooling system of the vehicle. Cooling system plays a crucial role in protecting the engine against the extreme temperature of the environment. Lack of adequate amount of coolant could cause breakdown of the engine due to overheating. So, quality and quantity of the coolant need to be inspected properly at a regular interval and if necessary should be replaced with suitable substitutes to increase the effectiveness of the cooling system. Apart from this, leakage of coolant has catastrophic effects on the performance of the vehicle and it is really essential to find the pinhole associated with the leakage of coolant and repair it in the first place. You may like to visit: http://www.cerroneseuropean.com/services
Thank you Elena, for the visit and sharing your insights about a car’s cooling system, your understanding of the subject is surprising as many folk are not that well informed.I followed your link and was pleasantly surprised by the professionalism and information on the website, I wish them all the best in going forward.
Gary
WHAT IS THE BEST PERCENT OF THE MIXTURE OF WATER AND COOLANT?
CAN WE USE ONLY COOLANT?
WE HAVE HUGE AIR WATER COOLER FOR GAS TURBINE MS5001 WHAT TO DO?
THANK YOU
Hello
Thanks for visiting my website, as to your question about mixture percentage, as coolant/antifreeze comprises of mostly water anyway, one could use just anti freeze, a generally accepted mixture is 50/50, some anti freeze brands are just more concentrated than others. I have never experienced any adversity using a strong anti freeze mix in all my 30+ years as an Auto Mechanic, I trust this answers your question and puts any doubt in your mind at rest.
Gary
Cooling system maintenance is one of the cardinal auto maintenance assignments that every car parent has to do on a regular basis to keep their automobile performing smoothly and to extend the life-expectancy and the efficiency of the engine. I think it’s a great way to ensure that all the fluid levels are at the requisite level. A vehicle’s cooling system consists of various components including- radiator, water pump, thermostat, bypass system, heater etc. A small negligence to the aftercare of cooling system can cause these components to perform jerkily. Thus, it is advisable to check the coolant and anti-freeze level, and each and every component of the cooling system in order to minimize the chance of mechanical failure by keeping the engine properly lubricated.
Thank you for your visit and your insights into the cooling system of a car and the importance of its up keep. Financial constraints could cause us as car owners to neglect our cars to a degree, but skimping on the cooling system could cause consequential damages, such as blown cylinder head gaskets or worse, engine failure, due to in adequate cooling.
Gary
To prevent your vehicle from over heating car cooling system is one of the safest and important cooling system that cool down the unbearable summer heat in the car. Radiator of the cars are mostly mounted in the front of the car and can be deteriorated with time and radiator fan which are essential part of cooling system constantly draws heat from the radiator core while the engine is running. It is also recommended to add anti freeze to your cooling system which not only help to regulate coolant temperatures but also lubricates the internal parts of the cooling system.